Building A WebRTC Voice & Video Chat App in 2024

“WebRTC is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 34.37% with market value above $ 300 Billion by 2031”
Heard of Flash and Licensing codecs?
These were the technologies that were used long before WebRTC came into existence.
So, is WebRTC so powerful to completely replace giant technologies?
Well, absolutely yes!
WebRTC is a big bundle of open-source frameworks and are greatly used to build Zoom-like and Skype-like apps.
Plus, with this technology, you can enable high-quality and low-latent connections between 2 or more browsers. Guess what, you do not need third-party plugins or software!
But is it really that easy to use?
As from what we know, a couple of years back, creating a web chat system was relatively a solid strain for developers.
The emergence and popularity of WebRTC have created immense potentiality for browsers to deliver and tackle peer-to-peer communication.
You might ask,
Will WebRTC make the development process simpler and quicker?
Well, the answer to this and a lot more will be discussed in the blog post below.
We shall also focus on the basics of WebRTC, its APIs, and the process of implementing video and voice chat with WebRTC. We will also cover the different servers behind this technology.
Table of Contents
How Does MirrorFly Bring Web Real-Time Communication (WebRTC) To You?
MirrorFly, a superlative in-app communication solution that offers 150+ WebRTC-enabled video, voice and chat SDKKs.
With these SDKs, you will be able to build impeccable live video calls, HQ voice and chat features into your web and mobile apps.
And the key reason why MirrorFly stands out in a competitive market is that it caters to developers of all expertise levels. How?
MirrorFly offerlive video chat apps 2 different pricing models:
- SaaS or Cloud solutions
- SaaP or Self-hosted chat solution
Browser & Mobile Signaling in WebRTC
Desktop:
Chrome, Firefox, Opera
Mobile:
Android & iOS support
Before getting into the building of a real-time WebRTC video chat app, let us be clear in identifying the functional dependencies to be used to build WebRTC Android/iOS and Web chat App.
Thorough WebRTC Library:
A complete WebRTC peer-to-peer native code package is required for every developer who wishes to use WebRTC API for chat app development for Android, iOS or web browsers.
jQuery
jQuery is used to handle the event manipulation and simplify the HTML with the easy to use APIs that work on several browsers.
Semantic UI CSS:
A framework used to contrive responsive layouts through human-friendly HTML with an elegant CSS framework that works on embellishing the user experience of the Chat Platform.
Handlebars
A compatible template provides the potential power to build semantic templates in HTML language. This brings significant changes in the mobile devices to embed simple WebRTC messaging features on Android and iOS platforms.
Apart from these dependencies, there are several frameworks and functionalities required to build a chat app with WebRTC enabled video and voice calling.
How Does Video/Audio Transmission of Chat Application take place?
Initially, both video and voice call functionalities depend on the streaming media between two client servers connected to each other.
Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is one of the most familiar and trusted standard techniques for voice and live video chat apps over the Web.
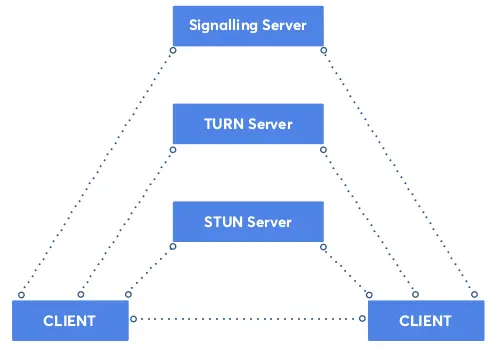
As we are very much aware of, WebRTC is the significant implementation for streaming media content from one client-server to another.
- Signaling
- STUN Server
- TURN Server
Signaling – Peer-to-Peer Connection
Signaling Websockets are used to set up call connections between the client servers. The client connection must adapt to each other by sending messages, data and media over the public IP address of both the clients webrtc signaling servers. To get the IP address, We use STUN Server.
STUN Server – Local IP Address
With the use of NAT (Network Address Translation) which provides the local IP address of the device to have peer to peer connection. To make this connection using WebRTC, we need to get the public IP address where STUN Server provides it.
TURN Server – Mediator
This server acts as a mediator to connect both the clients if case peer to peer fails. It sends data from one client to another over a signaling process. This methodology works for webRTC video and Audio calls on android/iOS chat app and also for media to create support for the WebRTC applications.
If you are about to integrate WebRTC into your Android/iOS chat app, then probably you must have a clear idea on three WebRTC APIs which plays crucial in developing your WebRTC voice/video chat on Android or iOS.
Now, let us dig deeper into WebRTC APIs.
Also Read: WebRTC FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
A Comprehensive Insight into WebRTC APIs for iOS/Android Chat Application
MediaStream
This allows you to obtain the access over the camera, screen or microphone of the device used by the user.
It also provides additional layers as a security, where it only allows access if the user is connecting from a (HTTP) secure connection. It allows the users to stream their entire media library.
This getUserMedia have three parameters namely:
- A Constraints object
- A Success Callback method
- A Failure Callback Method
RTCPeerConnection
This WebRTC allows the user to communicate directly to have a peer-to-peer connection, transcoding of the media files. It encodes and decodes the entire media content and voice / video chat that is sent to the remote server and from your local machine in receiving your media files.
RTCDataChannel
It helps in transferring the data directly between the two peer users connected in a bi-directional data channel. This also helps in creating a secure connection to send data at a real-time function.
Recommended Reading
Some of the Highlights that includes in implementing the Interface
Text Communication:
This allows the user to communicate over text in a real-time chat experience on all the Webrtc audio and video-enabled iOS/Android chat apps.
Voice Communication:
Based on Voice-over IP technology in real-time over the Internet through chat applications. Low latency is carried to make 1-to-1 or 1-to-many WebRTC voice chat app connections across all the devices.
Video Communication:
Video Connection helps in making quality WebRTC-enabled video and audio calls on Android/iOS chat apps continuously at low latency.
Adaptive bitrate reduces the complexity of video/audio chat at a high pixel rate.
Conclusion
These methodologies are quite bewildering right!
To make this more compatible and easier, MirrorFly is inbuilt with all these technologies and features embedded with WebRTC. This results in delivering a highly successful WebRTC-enabled Voice/Video Chat App that runs seamlessly on iOS/Android and Web browsers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a WebRTC video?
WebRTC (Web Real-time Communication) video is a technology that enables web-based applications to establish P2P audio/video connections and data transfer between browsers without the need for plugins or any third-party software. Moreover, WebRTC video uses Javascript APIs to seamlessly deliver high-quality, and low latent video and audio streams between web browsers thus making it an ideal choice for building video conferencing, live streaming, and other use cases.
Is WebRTC good for video calls?
Yes. WebRTC has proved to be the best and most widely adopted protocol for building real-time communication apps with video calling capabilities. It currently uses advanced video codecs to deliver low latent and high-quality video calls even under unstable network connectivity, and help an engineer build everything from a reliable video chat to an enterprise-level communication solution.
How does WebRTC video work?
WebRTC (Web Real-time Communication) is an open-source protocol that enables data transfer and real-time communication between browsers and devices using Javascript APIs.
Here’s how WebRTC video works:
– The first step is establishing a P2P connection across browsers using an SDP protocol that allows for data exchange in video, voice, or chat format.
– Next, the browsers start to gather ICE candidates that help browsers to connect with peers.
– As peers are located on a private IP network, WebRTC uses NAT traversal for browsers to reach each other.
– Finally, P2P moves across a relay TURN server and starts transmitting data.
Does WebRTC support chat functionality?
Yes. WebRTC does support chat functionality in addition to voice and video capabilities. With the WebRTC protocol, developers can easily build real-time communication apps, and add features like file sharing and screen sharing without installing any plugins or third-party software. Above this, the protocol is also compatible with all major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Opera.
What is the role of WebRTC in VoIP?
WebRTC is just an extension of VoIP
that makes video and audio calling, messaging, and P2P file transfer between mobile apps or web browsers seamlessly possible. It uses Javascript API to directly establish real-time communication between web browsers without the need to download any plugins or software.
Also Read: What is the Flutter WebRTC Plugin? A Complete Guide
What is the difference between VoIP and WebRTC?
WebRTC can be seen as an extension of VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) or a means to carry out VoIP. However, the real difference between the two is the underlying technology. VoIP uses a central server to route video/audio calls while WebRTC uses P2P architecture for establishing a connection. Secondly, VoIP requires the need of plugins whereas WebRTC enables real-time communication between browsers without any software or plugins installed.